Stepping into the world of web hosting can feel overwhelming, but cPanel makes it easy. This industry-standard control panel transforms complex server management into a simple, visual experience. Whether you’re launching your first site or managing professional emails, our cPanel for Beginners guide will help you navigate the dashboard with total confidence.
What is cPanel?
If you’re new to web hosting, cPanel is likely the first tool you’ll encounter.
cPanel is a web-based control panel designed to simplify the management of websites and hosting servers.
It provides a user-friendly, graphical interface (GUI) that allows website owners to perform complex technical tasks—such as creating email accounts, managing databases, and uploading files—without needing to use command-line tools.
Think of it as the dashboard for your online presence.
Getting Started with cPanel
- Access: You’ll typically find the login link to your cPanel in your hosting account welcome email or on your hosting provider’s website.
- Interface: cPanel has a clean, intuitive interface with icons representing different functions. Don’t be overwhelmed by the number of options; we’ll break it down.
Key Sections of cPanel
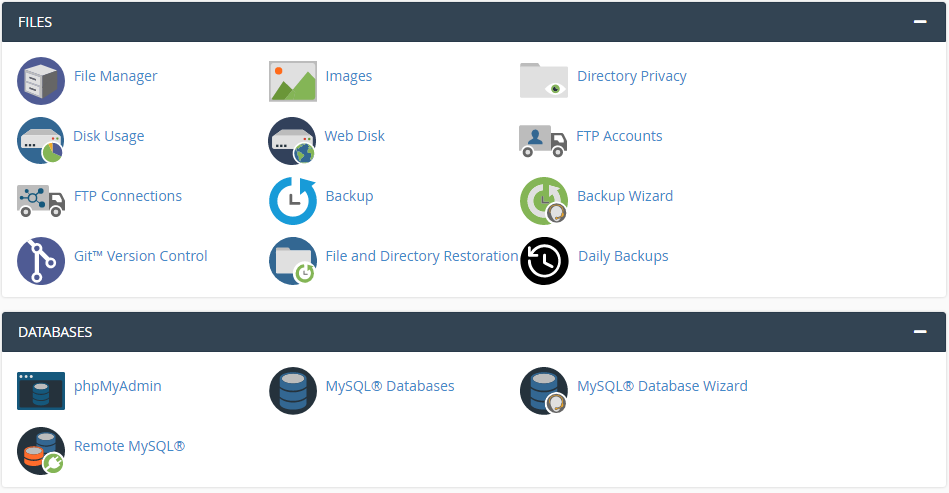
1. Files
This is where you manage the files that make up your website. You can upload, download, and edit files using a file manager similar to your computer’s.
- Public_html: The main directory for your website’s files.
- File Manager: A graphical interface to navigate and manage files.
- FTP Accounts: Create FTP accounts for others to access your files.
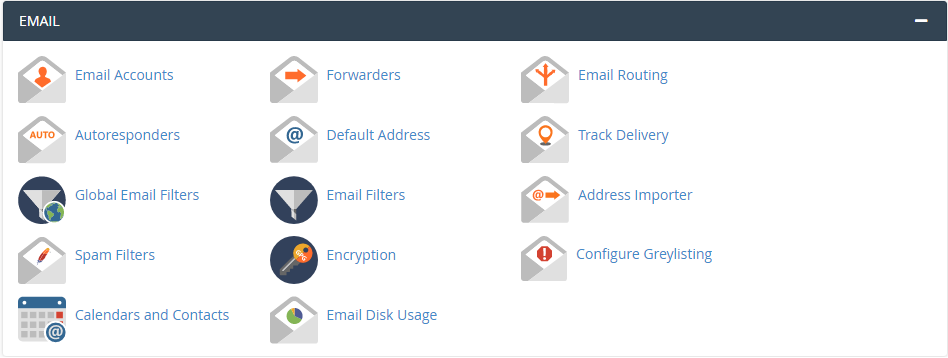
2. Email
Manage your email accounts, create email addresses, set up autoresponders, and more.
- Email Accounts: Create and manage email addresses.
- Forwarders: Set up email forwarding.
- Autoresponders: Create automatic email replies.
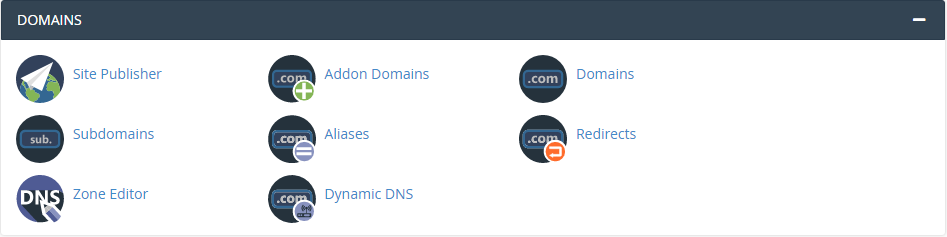
3. Domains
Manage your domain names, add subdomains, and point domains to your hosting account.
- Add-on Domains: Create additional websites under your main account.
- Parked Domains: Park multiple domains on a single website.
- Subdomains: Create subdomains like ‘blog.yourdomain.com’.

4. Databases
If your website uses databases (like MySQL for WordPress), you’ll manage them here.
- MySQL Databases: Create and manage databases.
- phpMyAdmin: A graphical tool to interact with databases.

5. Applications
Host Sonu offers a one-click installer for popular applications like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
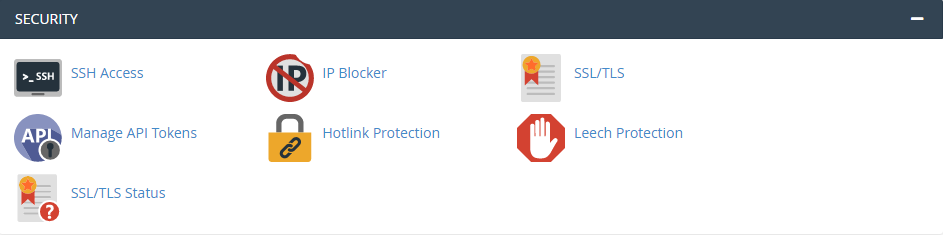
6. Security
Protect your website with various security measures.
- Security Center: Offers various security checks and tools.
- SSL/TLS Manager: Manage SSL certificates for secure connections.
- Hotlink Protection: Prevent others from directly linking to your images.
7. Metrics
Monitor your website’s performance and resource usage.
- Disk Usage: Check how much disk space you’re using.
- Bandwidth Usage: Monitor your data transfer.
- Statistics: View website traffic data.
Additional Tips
1. Start Slowly
Explore cPanel features gradually to avoid being overwhelmed.
2. Use Search
cPanel often has a search bar to quickly find specific functions.
3. Backup Regularly
Create regular backups of your website and database.
4. Update Software
Keep your website’s software and plugins updated for security.
5. Seek Support
If you encounter issues, don’t hesitate to contact Host Sonu support.
Conclusion
Mastering cPanel is a significant milestone in your web hosting journey. By moving beyond the initial intimidation of the dashboard, you’ve gained the power to manage your site’s files, emails, and security with confidence.
As you continue to explore, remember that every icon is a tool designed to simplify your digital life. Whether you’re launching a new WordPress site or optimizing your server performance, you now have the foundational knowledge to navigate your hosting environment like a pro. Keep experimenting, stay curious, and watch your online presence grow!


